How are DICOMs parsed?
The highest-level function to transform DICOM files into the unified, usable
datastructure Volume is the load_volumes_from_dicoms function.
Given a list of pydicom objects representing one or more DICOM instances, this
function automatically groups related DICOM instances (related in the sense of being
a part of a single 3D-volume) and constructs a Volume object for
each 3D-volume.
Internally, the function performs the following steps:
- Dismisses any invalid DICOMs: e.g. DICOMs with invalid pixel data, or PhoenixZIP report or localizers.
- Groups the DICOMs. In the case of slice-based DICOMs, each dicom object only
represents a single 2D slice of the 3D volume. DICOMs representing slices of
the same 3D volumes are therefore grouped together using either the
SeriesInstanceUID header tag, and, in the case of GE images, their diffusion
gradient directions and b_values. See
_get_partitions_of_3d_volumesfor more details. - Each partition of DICOMs is then converted into a
Volumeobject. This step utilizes thedcm2niixtool to convert the DICOMs into NIfTI files, and then uses the pixel data and affine matrix from the created nifti file to obtain the Volume object. DICOM header tag information is read using theReaderRegistryclass.
Reading DICOMs from different vendors
As DICOM files and their header structure varies significantly between vendors and even between different (software) models of the same vendor, a flexible and extensible mechanism to extract information from the DICOM headers is required.
!!! example
For example, the b-value of a diffusion-weighted image is stored in vastly different places depending on the vendor and software setting of the MRI machine:
- For Siemens 3D DICOMs, the b-value is stored in a tag inside the
PerFrameFunctionalGroupsSequencetags. - For Siemens slice-based DICOMs, the b-value is stored in the tag
0x0019, 0x100C. - For GE DICOMs, the b-value is stored in the tag
0x0018, 0x9087.
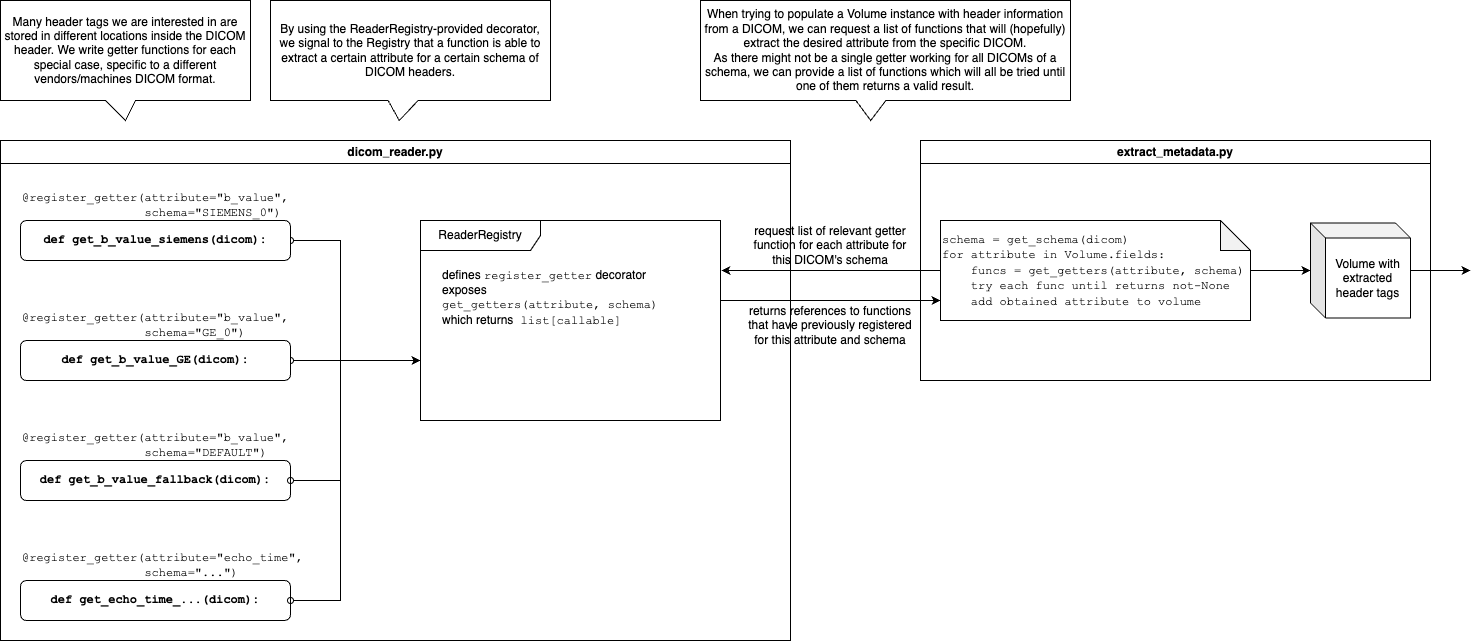
The ReaderRegistry class provides this mechanism.
-
Defines a
register_getter(attribute_name, dicom_scheme)decorator method: This decorator method "registers" the decorated function and indicates that the decorated function extracts a specified attribute from specified types of DICOM headers. Theattribute_nameargument is the name of the attribute that the function extracts, and thedicom_schemeargument is aVolumeSchemeenum instance that indicates for which type of DICOM header the decorated function is compatible. -
Provides the
get_getters(attribute_name, dicom_scheme)function. It returns a list of functions that are registered to extract the attributeattribute_namefrom DICOM headers of typedicom_scheme.- The
get_getters_in_priorityfunction is a wrapper around theget_gettersfunction that returns the list of all getter functions for specified attribute in order of priority. Meaning: getters specifically marked for the specifieddicom_schemeare returned first, followed by all getter functions registered to thedefaultscheme, followed by all other getter functions.
- The
-
In
get_all_header_data, theget_getters_in_priorityfunction is used to obtain the getter functions for each attribute that should be extracted from the DICOM headers. The getters for an attribute are called in this order until one of them returns a non-None value. For slice-based DICOMs, the function first passes all DICOM object for the 3D volume to registered getters. Following this "first round" of execution of getters, the function passes only the first DICOM object in the list to the getters. For 3D DICOMs, this single DICOM object is only passed once to the getters.
The consequence of this design is the following:
For each attribute that should be extracted from DICOM headers and stored in
the Volume object, a getter function needs to be written. The getter can be
scheme-specific, or simply be registered to the default scheme. The getter
should be defined in the dicom/dicom_reader.py file.
This makes adding support for new DICOM header formats and new attributes to
extract very easy. :)